Assessment consulting for successful security strategies
How do you get an objective overview of existing cyber attacks and vulnerabilities in the IT infrastructure?
Different companies – different starting scenarios: no two infrastructures or corporate risks are the same. The most dangerous cyber threats are individually designed for the vulnerabilities of the company in question. Our expertise and regular security assessments provide you with an overview of your security status and adherence to existing, sector-specific security standards.
We help you with or perform risk assessments, vulnerability assessments, penetration tests and audits for you. To do so, we use the latest standards of ISO 31000:2018 or B3S, as well as market-leading tools.
-
Risk assessment
Identify, assess, control, review
-
Vulnerability and penetration testing
Revealing vulnerabilities in companies - Penetrationstests, Vulnerability Scans and Cyberscoring
-
Audit / ISMS
Pre-audit, planning, certification
Risk Assessment
The foundation for a successful IT security strategy is laid in the risk assessment. In accordance with the applicable risk management standards of ISO 31000:2018, ISO 14971:2013, or B3S, plus others, we perform a four-stage risk assessment:
- Vulnerability identification
- Risk analysis
- Risk evaluation
- Risk monitoring
Here, our experts look at the relevant assessment methods for the sector, corporate organization and structure, and thus make completely sure that the risk assessment is precisely suited to your needs.
Vulnerability Management
Cyber Scoring, Vulnerability Scans and Pentests
Whether due to the growing threat situation and increasingly sophisticated attack techniques or the requirements of certifications and audits - a regular review of the implemented protective measures is indispensable.
You can meet these requirements with penetration tests and vulnerability scans. Many customers also use automated cyberscoring to obtain an overview.


Cyber scoring assesses an organization's security posture using metrics and key performance indicators. It can be used to track improvements over time.
A vulnerability scan is a targeted search for security holes and vulnerabilities in a network, application or system. The purpose is to identify known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Penetration tests are targeted attacks on a system to test the actual exploitability of vulnerabilities. They simulate an attacker's approach to check whether it is possible to penetrate a system and compromise data.
- Implementation: Using automated tools and algorithms.
- Focus: Assess security status and identify high-level risks.
- Implementation: Automated using tools such as Nessus, Burp Suite or similar.
- Focus: Focus on identifying vulnerabilities that need to be addressed to improve security.
- Execution: Manual. These tests are performed by specialized security experts (penetration testers) who use various attack techniques to identify vulnerabilities and demonstrate how they can be exploited.
- Focus: The focus is on identifying vulnerabilities and how they can be exploited to address specific security issues.
Penetration testing workflow

When the pen test is performed, it produces valuable strategic information for your IT and, at the same time, legal verifications for statutory requirements.
Types of pentests offered by Consist:
- Infrastruktur (including Active Directory and LDAP)
- Web / Intranet / Web-API (Rest, SOAP, …)
- Cloud (AWS, Azure, Google)
- Mobile (Android, IOS, MDM)
- Wireless (Wlan, Bluetooth, NFC, RFID)
- IoT / OT / Hardware
- Phase 1: Preparation
Before the actual tests and scans begin, the relevant legal conditions and other requirements as well as the exact scope of the test must first be specified in Phase 1. Once all the organizational framework conditions have been negotiated, phase 2 can begin. - Phase 2: Reconnaissance
In this stage of the penetration test, the test object is analyzed using initial analyses such as port scans and footprinting. Furthermore, automated scanning tools are used in this phase to gather as much information as possible about the test object and to perform initial automated attacks on the systems. Based on the results of the tools used, the first potential vulnerabilities can be identified, which have already been determined automatically by the tools. Based on this information and the analysis from phase 3, further manual attacks are then carried out in phase 4. - Phase 3: Enumeration
The corresponding scan results are evaluated and analyzed. On the one hand, this reveals the attacks already executed by the tools, and on the other hand, the information collected from the scans can be used to execute manual attacks in phase 4. - Phase 4: Exploitation
Based on the scan results from phase 2 and the more detailed analysis in phase 3, further manual attacks are carried out on the test object. In this phase, attempts are made to exploit vulnerabilities, for example to carry out attacks to extend privileges (privilege escalation) or to generally check privileges (access control). In addition, further attacks such as XSS or SQL injection are carried out. - Phase 5: Documentation
Finally, the vulnerabilities and findings are evaluated and documented based on CVSSv3.1, taking into account the probability of exploitation, the severity of the vulnerability and other parameters to generate a corresponding risk score.
Cyber Scoring
The external view of an attacker:
Cyber scoring uses Framework and publicly available data from intelligent open source tools and technologies (OSINT) to capture information the way attackers also use it.
Cyber scoring provides you with a management report at your disposal that simultaneously serves as documentation and an effectiveness check (GDPR compliant).
The fully automated scoring provides information on the following categories:
- attack surface on the Internet
- configuration of the web servers
- cyber security score
- specific vulnerabilities
- reputation in cyberspace
- organizational and process risks
- country risks
- trusted encryption
Under "organizational and process risks" you can find out, for example, how well your service providers are prepared with regard to legal requirements (ISO 27001, ISO 9001, GDPR).
Audit
Standards create trust.
ISO 27001 has been around since 2005, and is an internationally recognized standard with which companies are not only able to substantiate strict IT security requirements, but also the implementation of specific IT Grundschutz measures.
ISO 27001 is the leading international standard for evaluating the security of information and IT environments. A central requirement for ISO 27001 and a main prerequisite for certification is the introduction of an Information Security Management System, or ISMS for short. The ISO 27001 standard prescribes requirements for implementing and documenting an ISMS. Accordingly, the ISMS defines rules and methods to not only guarantee information security, but also to be able to optimize it.
Consist - Information Security Management System - ISMS
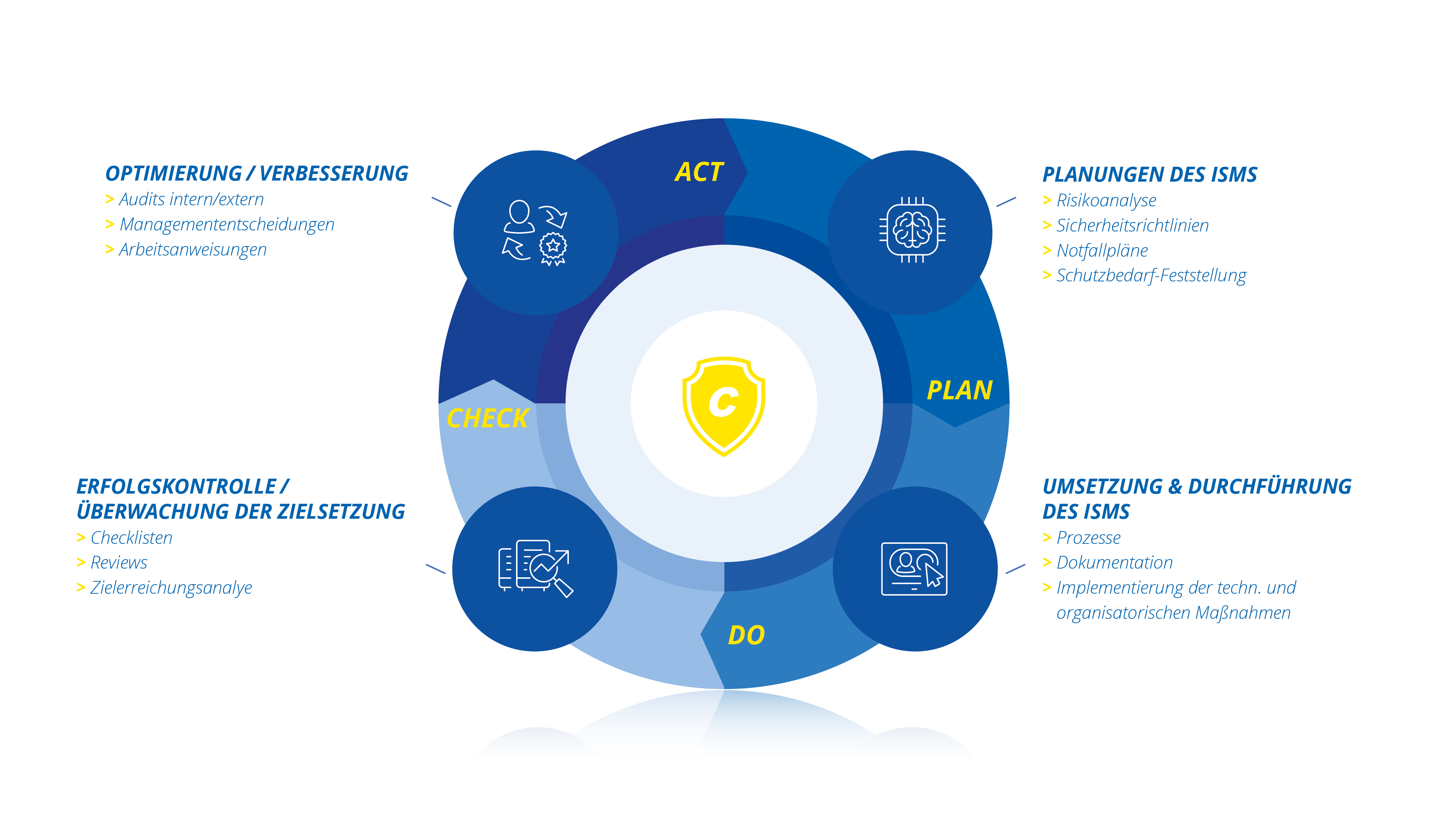
Companies profit from an Information Security Management System in several ways:
- Statutory requirements like compliance regulations are met
- Stakeholders’ trust is strengthened
- Audits are made easier
- Greater security and performance of IT systems is achieved
Our consultants receive regular training and hold personal certification for:
- ISACA ISMS Auditor / Lead Auditor in accordance with ISO/IEC 27001:2022
- Additional auditing procedure competence for Section 8a of the Act on the Federal Office for Information Security (BSIG)
- Data security officer (TÜV)
- compTIA Security+
- IPMA Level D (GPM)
We consult, implement and assist you with the introduction and certification of an ISMS.
KRITIS companies
If we take a look at the operators of critical infrastructure (KRITIS companies), there are still no specific specifications for introducing an ISMS, however, KRITIS companies must provide verification of IT security every two years in the form of security audits or certification. Introducing an ISMS in accordance with ISO 27001 is currently the best solution for this and it is now mandatory for electricity and gas network operators according to IT security laws.
In its orientation guide (OH) for the implementation of attack detection systems (SzA), the German Federal Office for Information Security (BSI) recommends the establishment of an ISMS for this reason.
Kritis Services
We provide assistance with or conduct the following for you:
- Training courses and awareness training
- Security audits
- Creation and maintenance of a rule base
- Risk management
- Supervision with external audits
- Support with the introduction of an ISMS
- External ISMS officer
Your contact

Joscha Sternadel
Portfolio Manager
phone: +49 431 3993-775
mobile: +49 162 2130358
e-mail: sternadel@consist.de

